|
|
|
|
Bean
PWMMC
|
Pulse width modulation for motor control
Application Notes, Tips and Tricks for the bean. Hints for code optimization.
|
Application Notes:
Align
The Align selects either Center-Aligned or Edge-Aligned PWMMC generator outputs.
The center-aligned mode is shown on Figure 1. and
the edge-aligned mode is shown on Figure 2..
Period in the center-aligned mode is two times longer then in the
edge-aligned mode.
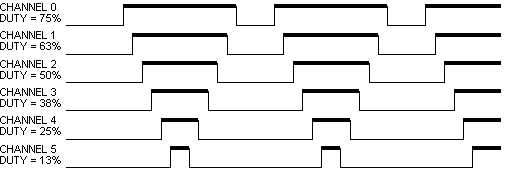 Figure 1. PWMMC Center-Aligned Mode
Figure 1. PWMMC Center-Aligned Mode
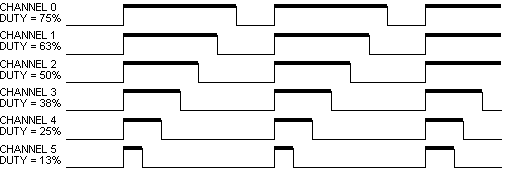 Figure 2. PWMMC Edge-Aligned Mode
Figure 2. PWMMC Edge-Aligned Mode
Mode
The Mode selects either Complementary Channel Operation (see Figure 3.)
or Independent Channel Operation (see Figure 1.) PWMMC generator outputs.
The complementary chanel operation drives top and bottom transistors in an inverter circuit, such as the one in
Figure 4..
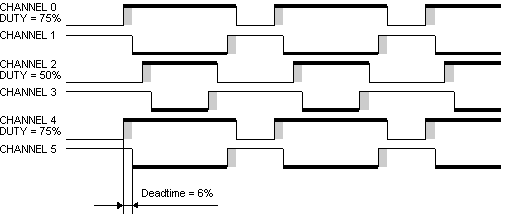 Figure 3. Complementary Channel Operation
Figure 3. Complementary Channel Operation
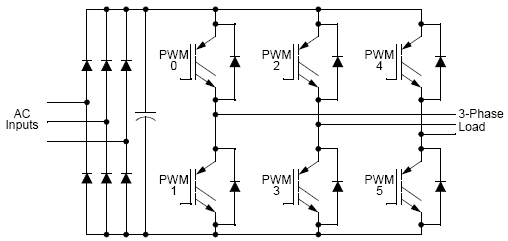 Figure 4. Typical 3-Phase Inverter
Figure 4. Typical 3-Phase Inverter
Output Pads
The PWMMC output Pads can be enabled or disabled by property Output Pads.
The power-up default has the pads disabled. This settings does not affect the functionality of the
PWMMC, so the PWMMC module can be energized with the output pads disabled. The Output Pads can be
changed by the OutputPadEnable() and OutputPadDisable() methods. When the Output Pads
are disabled the PWMMC pins are set to the tri-stated.
Frequency / Output Frequency
The Frequency of the PWMMC output is set by this property. The right output frequency is shown in
Output Frequency.
Frequency in the center-aligned mode is half then in the
edge-aligned mode (see Figure 5.).
 Figure 5. Frequency in Center-aligned/Edge-aligned mode
Figure 5. Frequency in Center-aligned/Edge-aligned mode
The PWMMC output frequency can be set by the SetPeriod() or SetPrescaller() methods.
Both methods is low-level methods and write the value of the parameter into register of the CPU.
The Value for setting Frequency property can be shown by the Peripheral Initialization Inspector
(see Figure 6.).
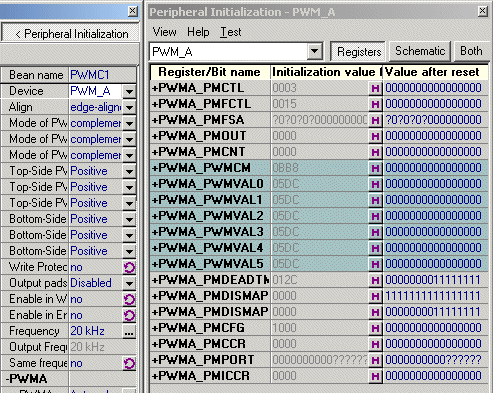 Figure 6. Peripheral Initialization Inspector
Figure 6. Peripheral Initialization Inspector
Dead-time
While in the Complementary mode, each PWM pair can be used to drive top/bottom
transistors, illustrated in Figure 4..
Ideally, the PWM pairs are an inversion of each other. When the top PWM channel
is active, the bottom PWM channel is inactive and vice versa.
To avoid short circuiting between top and bottom transistor, there must be no overlap of
conducting intervals between top and bottom transistor. But the transistorís characteristics
make its switching-off time longer than switching-on time. To avoid the conducting
overlap of top and bottom transistors, dead-time needs to be inserted in the switching
period.
Dead-time generators automatically insert software-selectable activation delays into each
pair of PWM outputs. The Pulse Module Dead-time (PMDEADTM) register specifies the
number of PWM clock cycles to use for dead-time delay. Every time the PWM generator
output changes state, dead-time is inserted. Dead-time forces both PWM outputs in the pair
to the inactive state. The dead-time is shown in Figure 3..
Duty
This property set the pulse width. In the real-time the Duty is set by SetDuty(), SetDutyPercent(),
SetRatio15() and SetRatio16() methods. The SetDuty() method is low-level method and
set the registers of the PWMMC. The Value of SetDuty() method parameter is availabled by
the Peripheral Initialization Inspector (see Figure 6.).
The Value of duty is shown in Figure 1.,
Figure 2., Figure 3.
by the thick line.
Reload / Half Cycle Reload
This property selects the PWMMC load frequency according Table 1.. Half Cycle Reload property
enables half cycle reloads only in Center-Aligned mode. Half Cycle Reload has no effect on Edge-Aligned mode.
Table 1. PWMMC Reload Frequency
| Value |
PWMMC Reload Frequency |
Value |
PWMMC Reload Frequency |
| 0 |
Every PWMMC Opportunity |
8 |
Every 9 PWMMC Opportunity |
| 1 |
Every 2 PWMMC Opportunity |
9 |
Every 10 PWMMC Opportunity |
| 2 |
Every 3 PWMMC Opportunity |
10 |
Every 11 PWMMC Opportunity |
| 3 |
Every 4 PWMMC Opportunity |
11 |
Every 12 PWMMC Opportunity |
| 4 |
Every 5 PWMMC Opportunity |
12 |
Every 13 PWMMC Opportunity |
| 5 |
Every 6 PWMMC Opportunity |
13 |
Every 14 PWMMC Opportunity |
| 6 |
Every 7 PWMMC Opportunity |
14 |
Every 15 PWMMC Opportunity |
| 7 |
Every 8 PWMMC Opportunity |
15 |
Every 16 PWMMC Opportunity |
Mask fault x
Fault protection can disable any combination of PWMMC pins. Faults are generated
by a Logic 1 on any of the FAULT pins. Each FAULT pin can be mapped arbitrarily
to any of the PWMMC. When fault protection hardware disables PWMMC pins, the PWMMC generator
continues to run, only the output pins are deactivated. The fault decoder disables PWMMC
pins selected by the fault logic and the disable masking property. Please see
Figure 7..
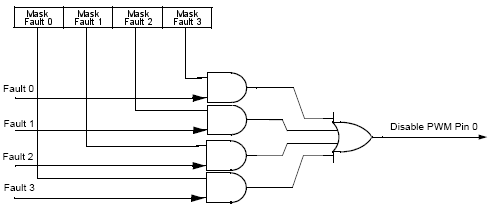 Figure 7. Fault Decoder for PWMMC Channel 0
Figure 7. Fault Decoder for PWMMC Channel 0
Fault Clearing Mode
This property selects automatic or manual clearing of FAULTx pin faults.
When the Clearing mode is set to manual, the fault flag must be clear by the
ClearFaultFlag() method.
|
|
|
Processor ExpertTM and Embedded BeansTM are registered trademarks of UNIS, Ltd.
©1997-2005, UNIS, Ltd.
|
|
|